Learn how cybersecurity works for small startups, from securing networks and data to preventing cyber threats with simple, affordable solutions.
Introduction
Today, digital tools are essential for how businesses operate and grow. From email and payment to customer management, technology shapes daily operations. Yet, this reliance makes small startups especially exposed to cyber risks. Cybercriminals continuously seek ways to exploit weaknesses, putting small businesses at the forefront of evolving threats.
Unlike large corporations, small businesses often lack dedicated cybersecurity teams or advanced infrastructure, which makes them attractive targets for hackers.
Why Is Cybersecurity for Small Businesses Critical?
Many small businesses mistakenly believe that cybercriminals only target large organizations. In reality, hackers often focus on small businesses because they typically have weaker security controls, outdated systems, and limited awareness of cyber risks. This makes them easier to breach.
A single cybersecurity incident can have devastating consequences. Data breaches may expose sensitive customer information such as personal details, passwords, or payment data. Financial losses can occur due to fraud, ransom payments, legal penalties, or operational downtime. In many cases, the reputational damage caused by a breach can be even more harmful than the financial loss, as customers may lose trust and choose competitors instead.
Cybersecurity also helps small businesses comply with legal and regulatory requirements related to data protection and privacy. Strong security practices demonstrate professionalism, responsibility, and commitment to customer safety, all of which are essential for sustainable growth and long-term success.
Impact of Cyber Threats on Small Business Operations
Cyber threats can significantly disrupt daily business operations and create long-lasting challenges. One of the most immediate impacts is downtime. When systems are compromised, businesses may lose access to essential tools, customer records, or financial systems. This interruption can delay services, reduce productivity, and lead to dissatisfied customers.
Data breaches are another major concern. When confidential information is exposed, businesses may face legal consequences, regulatory fines, and costly recovery processes. Restoring systems, investigating breaches, and notifying affected customers require time, money, and expertise that many small businesses struggle to afford.
Cyber attacks can also damage employee morale and customer relationships. Employees may feel insecure about using company systems, while customers may hesitate to share personal information. Over time, repeated or severe incidents can weaken a business’s market position, making it difficult to recover and grow in a competitive environment.
Key Cybersecurity Measures for Small Businesses
Enhancing Employee Awareness and Involvement
When it comes to cyber risks, employees are frequently the first line of defense. Many attacks, such as phishing and social engineering, rely on human error rather than technical weaknesses. Training employees to recognize suspicious emails, fake links, and unusual requests can significantly reduce risks.
Regular cybersecurity awareness programs help create a security-conscious culture within the organization. When employees understand their role in protecting company data, they are more likely to follow best practices such as using strong passwords, reporting suspicious activity, and following security guidelines. Employee involvement transforms cybersecurity from a technical task into a shared responsibility.
Technology in Enhancing Cybersecurity Measures
Technology plays a crucial role in strengthening cybersecurity defenses. Firewalls act as barriers between internal networks and external threats, while antivirus and anti-malware software detect and remove malicious programs. Encryption ensures that sensitive data remains unreadable even if it is intercepted by unauthorized parties.
Secure authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), add an extra layer of protection by requiring users to verify their identity using multiple factors. Regular software updates and security patches are equally important, as they fix known vulnerabilities that attackers often exploit. By combining the right tools with proper configuration, small businesses can significantly improve their security posture.
Common Cyber Threats Faced by Small Businesses
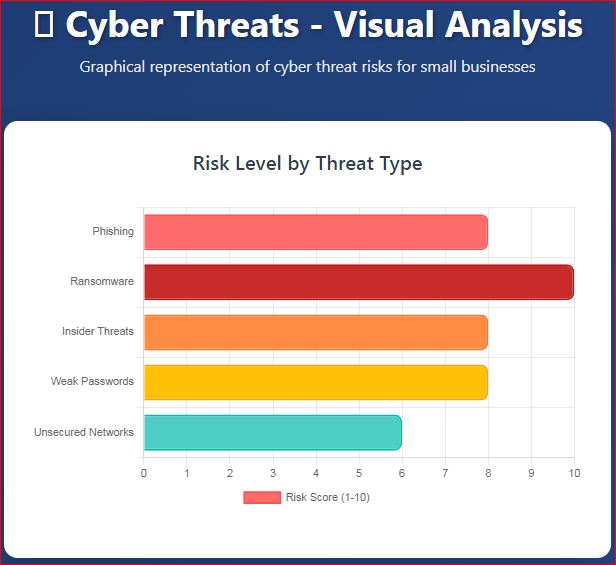
1. Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks trick employees into sharing login details or clicking on malicious links.
They usually appear as genuine emails, messages, or websites. These attacks target human error rather than technical weaknesses. Employee awareness is the best defense against phishing threats.
2. Ransomware
Ransomware encrypts business data and demands payment for its release. It can completely stop daily operations and cause financial loss. Paying the ransom does not always recover the data. Regular backups and strong security tools help prevent ransomware.
3. Insider Threats
Insider threats come from employees or internal users. They may occur due to negligence or intentional misuse of access. Weak passwords and a lack of training increase insider risks. Access control and monitoring reduce these threats effectively.
4. Weak Passwords
Hackers can easily guess or crack weak passwords. They provide quick access to business systems and data. Using simple or repeated passwords increases cyber risk.
Strong password policies improve overall security.
5. Unsecured Networks
Unsecured networks allow unauthorized users to access systems. Public Wi-Fi often exposes data to cybercriminals. Lack of encryption makes networks vulnerable to attacks. Securing networks prevents unauthorized access and data theft.
Essential Components of a Comprehensive Cybersecurity Strategy
1. Risk Assessment
Risk assessment helps identify vulnerabilities in systems and networks. It allows businesses to understand where security weaknesses exist. Regular assessments help prioritize security improvements. This process ensures better use of time and resources.
2. Strong Password Policies
Strong password policies prevent unauthorized system access. They require complex, unique passwords for all users. Regular password updates improve security. This reduces the risk of hacking and data breaches.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA strengthens the security of login procedures. It requires more than one verification method. Even if passwords are stolen, access remains protected.
MFA greatly reduces unauthorized access risks.
4. Employee Cybersecurity Training
Employee training increases awareness of cyber threats. It helps staff recognize phishing and social engineering attacks. Regular training keeps employees updated on best practices. Informed employees strengthen overall business security.
5. Incident Response Planning
Incident response planning prepares businesses for cyber attacks. It outlines steps to detect, respond, and recover quickly. Quick action reduces damage and downtime.
This plan ensures smoother recovery after incidents.
6. Cybersecurity Tools and Services
Cybersecurity tools protect systems from malware and attacks. Professional services provide expert monitoring and support. They help maintain updated and strong security defenses. This ensures continuous protection and business confidence.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is vital for small startups. As digital reliance increases, so do attacks. One incident can cause financial, operational, and reputational loss. Being proactive protects what matters most—your business and customers.
By understanding common threats, training employees, adopting reliable technologies, and implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, small businesses can significantly reduce risks. Cybersecurity is not just about protecting data; it is about ensuring business continuity, maintaining credibility, and supporting long-term growth. Investing in cybersecurity today builds a safer, more resilient foundation for tomorrow’s success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Are small businesses really targeted by cybercriminals?
Yes. Small businesses are often targeted because they typically have fewer security measures, making them easier to attack than large organizations.
2. What is the most common cyber threat for small businesses?
Phishing attacks are the most common, as they rely on tricking employees into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware.
3. Is cybersecurity expensive for small businesses?
Cybersecurity can be affordable when implemented strategically. Many cost-effective tools and solutions are available that provide strong protection without large investments.
4. How often should employees receive cyber security training?
Employees should receive training at least annually, with regular updates whenever new threats or security policies are introduced.
5. What should a business do after a cyber attack?
The business should follow its incident response plan, isolate affected systems, assess damage, restore data from backups, and review security measures to prevent future attacks.



After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.